There are several programs for mask-design used in lithography; L-Edit, Clewin, IntelliCAD, and Klayout. In the university that I attended, staffs in clean room recommended using "Klayout" because of its simplicity and open-source program*. So, here, I will summarize the basic scheme of how to use Klayout.
1. What is Klayout?
Simply, Klayout provides a function of modifing GDS (Graphic Design System) files. Especially, Klayout is widely used as a EDA (electronic design automation) tool for IC designs. This program can be linked to Python.
1.1. Advantages of Klayout
(1) Powerful layout editing function
(2) Provide a various file format
(3) Scripting and automation
(4) High quaility of DRC(Design Rule Checking)
(5) Powerful visulization and analyzing tools
2. Install Klayout
Download a Klaoyout installing file consistent with your OS from the official website; https://www.klayout.de/build.html
3. How to use Klayout with an example of drawing a simple SAW
Even though there are well-documented user Manuals in the official website, I'll demonstrate an example step by step to show how newbies like me can use kLayout. Let's suppose that we want to draw a simple SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) device. The brief information about what is the SAW can be found in the wikipedia.
The basic design of SAW is as follows;

Specifically, I want to design the SAW device with the following specific dimensions;
▪ The size of IDT fingers : 8.7$\mu$m
▪ The distance between two nearest IDT fingers : 8.7$\mu$m
▪ The number of IDT fingers on input and output transducers: 1cm
▪ The size of each IDTs: 0.696mm x 4mm x 70nm
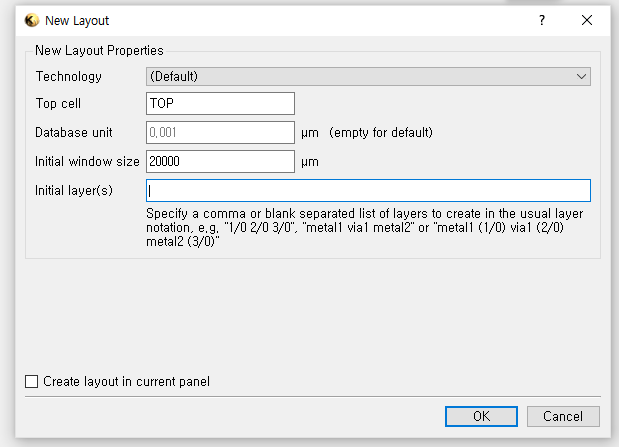
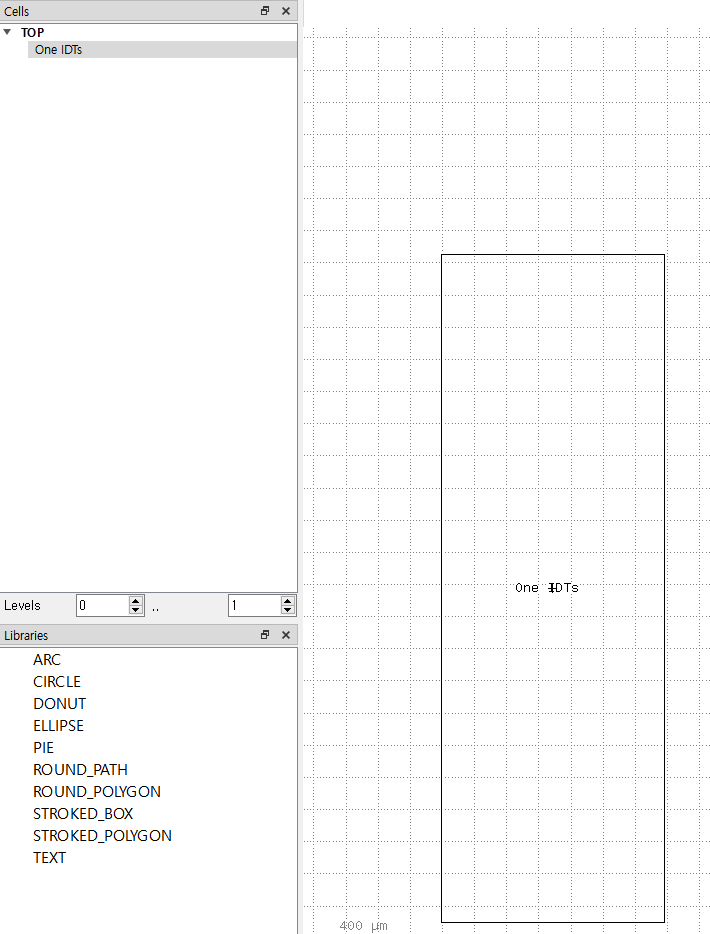
3.1. Open files and make a new layout
(1) Open "Klayout (Editor)"
(2) Make a new layout: `File` > `New layout`

3.2. Create Layers
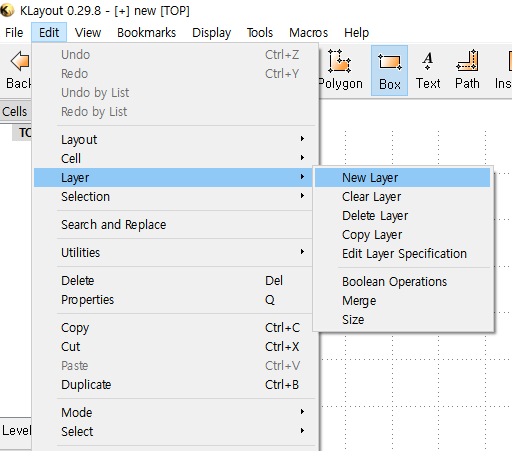
If you open Klayout first after installation, you don't have any layers in the right panel. In order to draw any objects in the middle panel, you need to create a specific layer for your objects. Wthout selecting a layer, you can not draw anything.
(1) Create Layer: `Edit` > `Layer` > `New Layer`
(2)
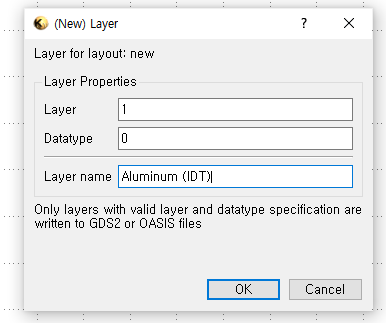
NOTE: Layer Properties
(1) Layer:
(2) Datatype:
- the datatype can be assigned as a single number between 0~63.
- By choosing the different datatypes, you can specify a material in the same "Layer"
3.3 Draw objects
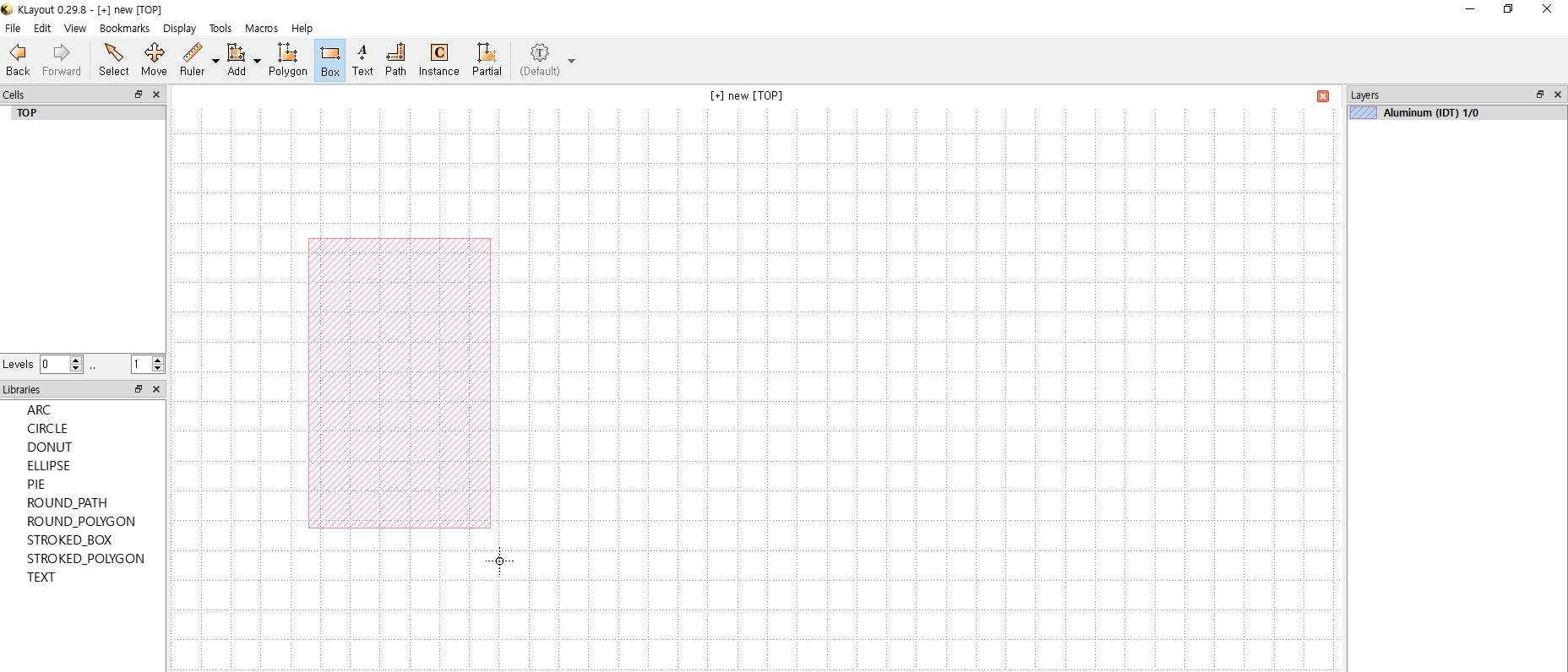
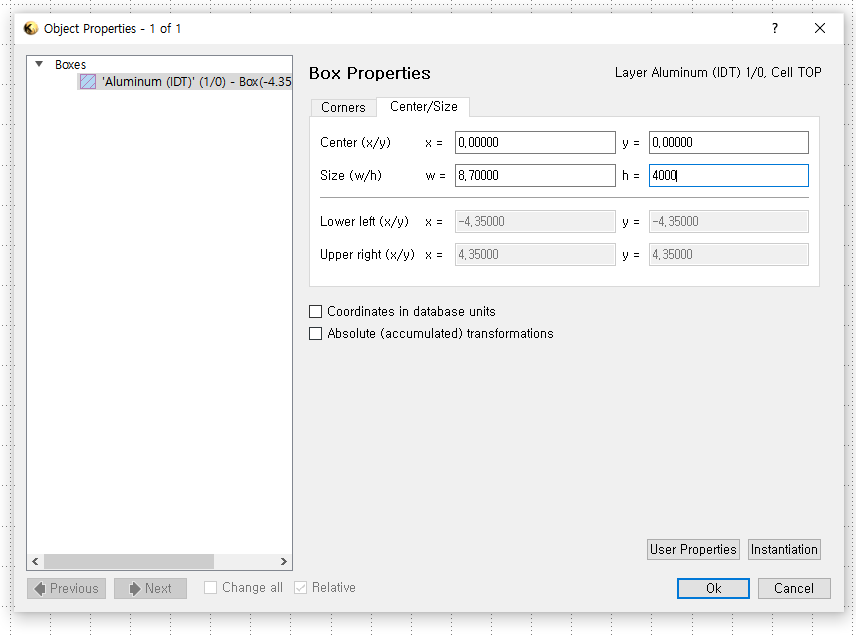
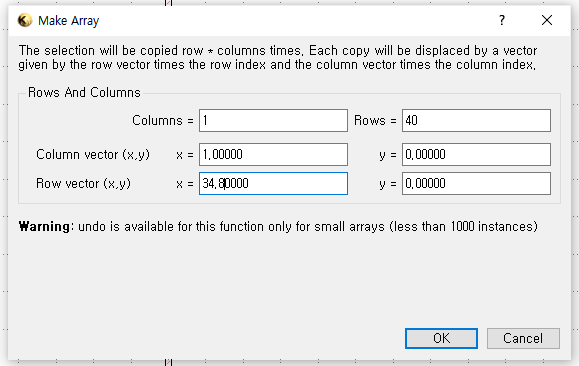
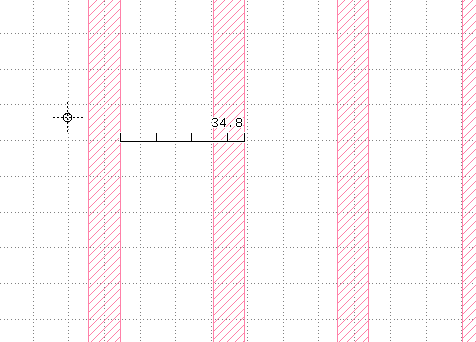
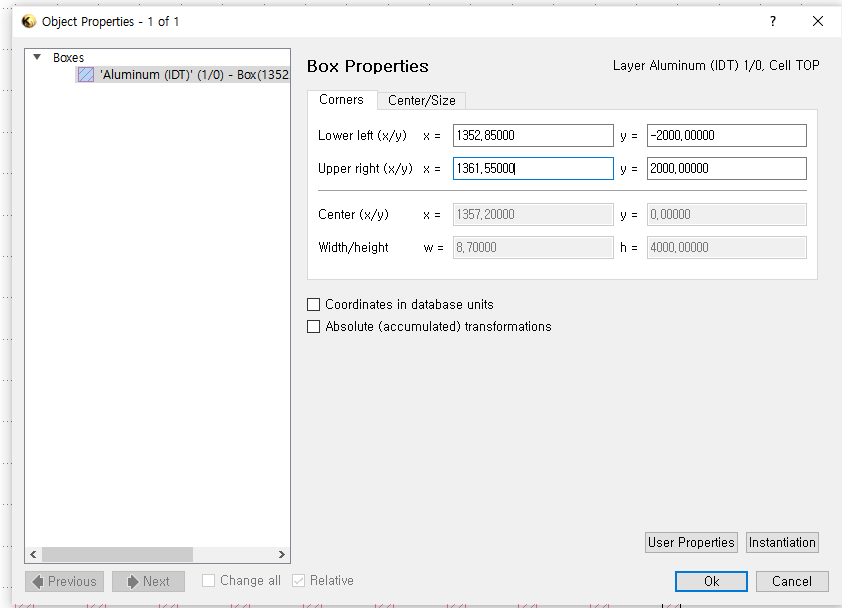
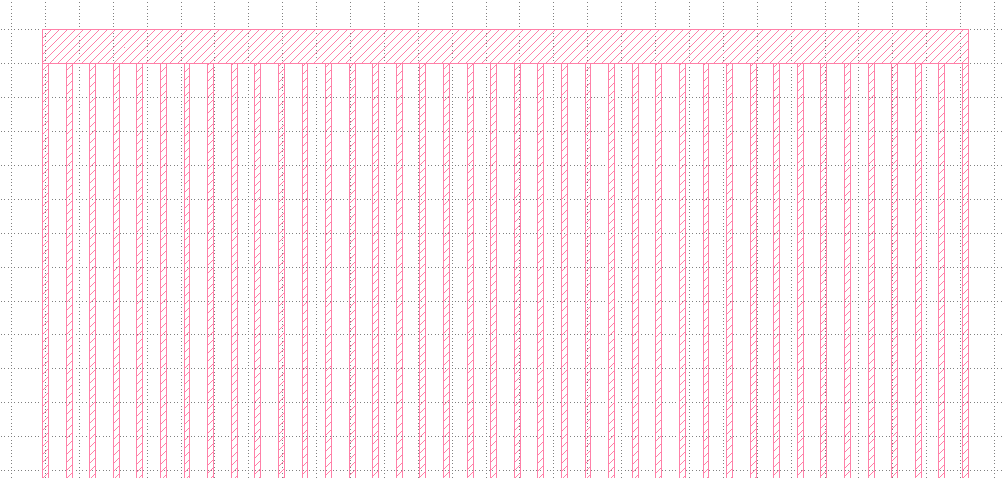
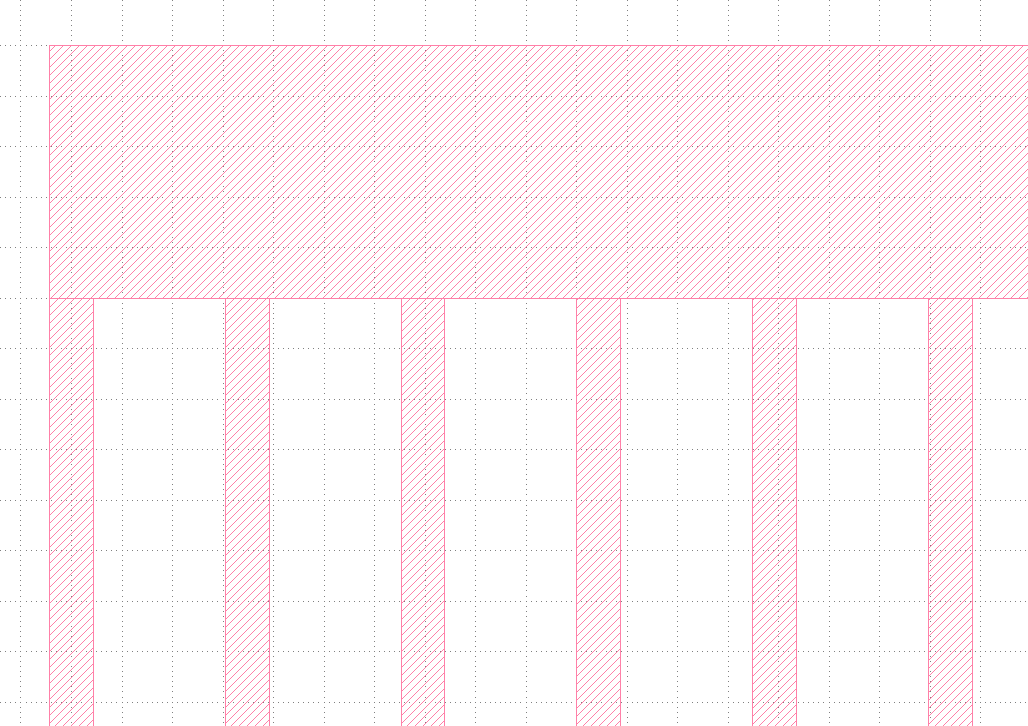
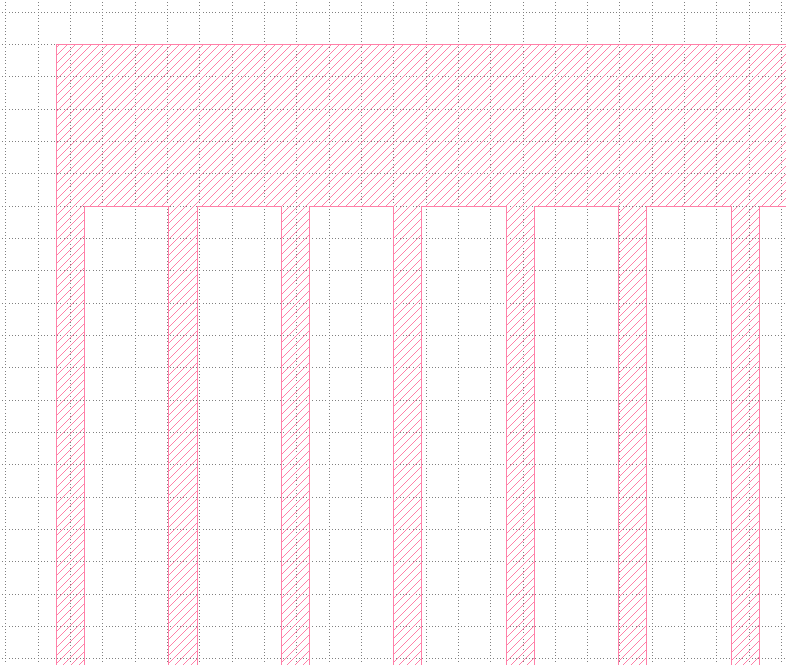
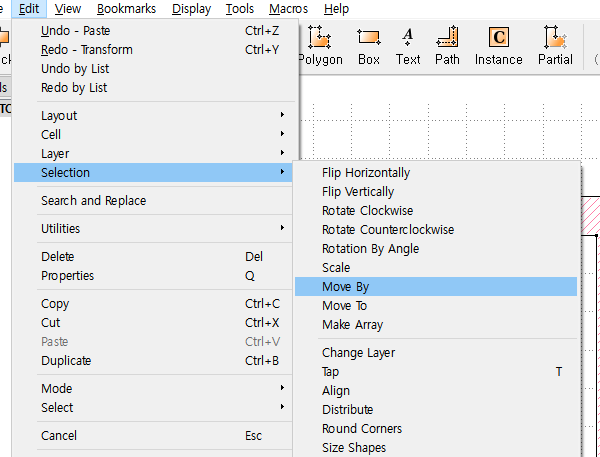
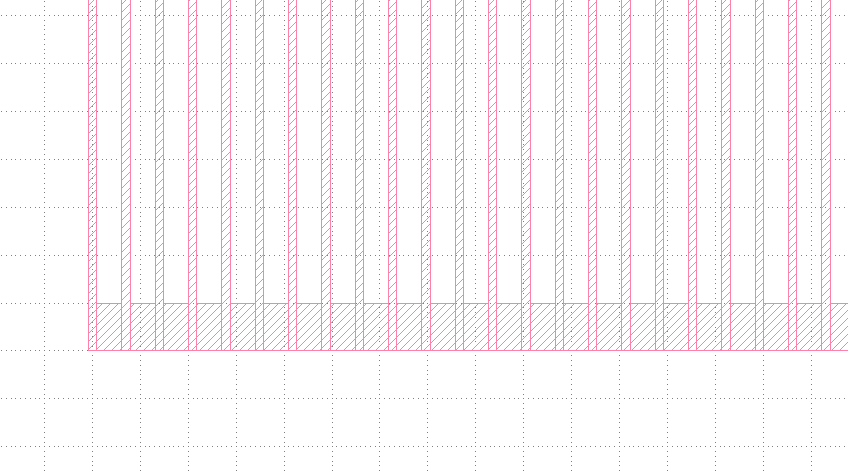
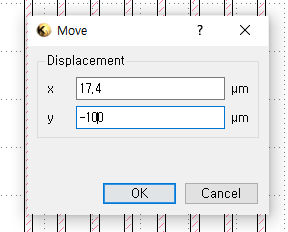
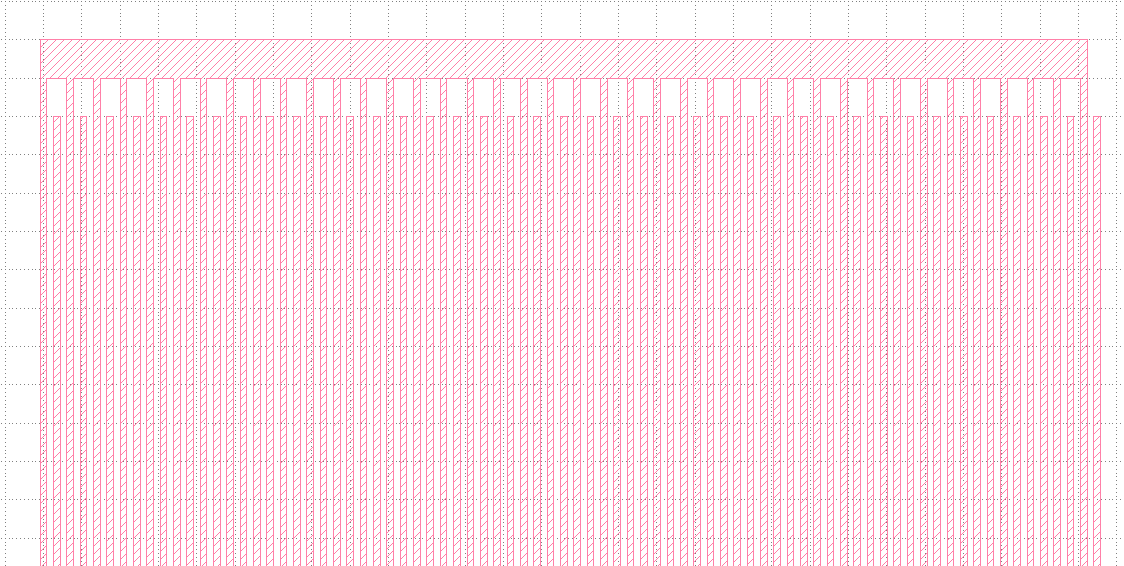
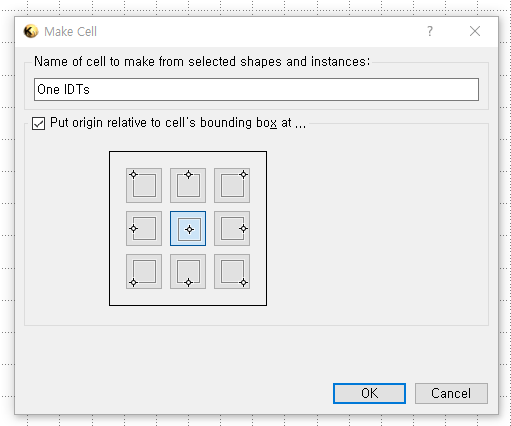
`Edit` > `Selection` > `Make Cell`
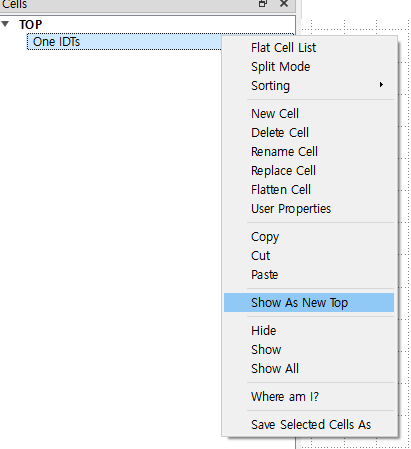
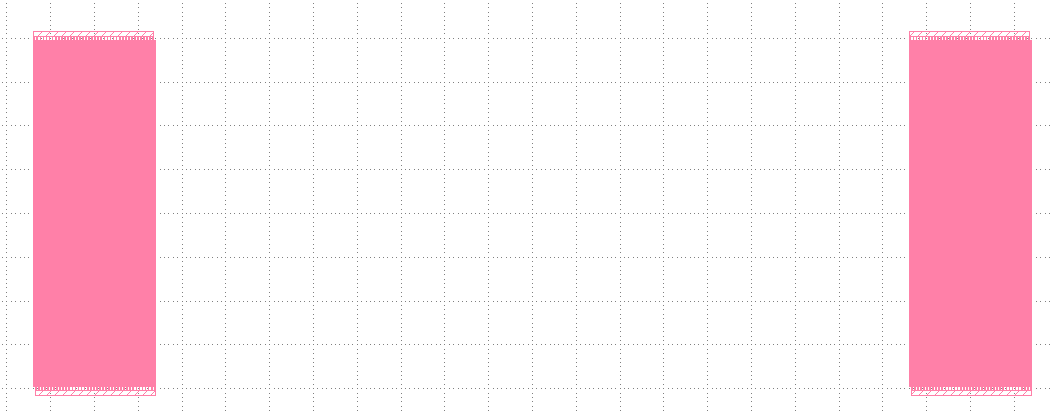
NOTE:
(1) `Shift` + mouse: move the object horizontally
(2) `Ctrl` + mouse: move the object vertically
NOTE: `Cell` function
NOTE: The GDS format requires that a single object should be drawed by a single line. Therefore, if a void exists inside the object, you can see a line connecting the circumference of the void and the outer surface of the object.
3.4. Save the file
Note that if you save your file as GDS2 or OASIS, then the information about layer names are not saved in the same file. Therefore, you need to save another file having layer names. This file extension is ".lyp".
(1) Save layer property: `File` > `Save Layer Properties`
(2) Save your file as GDS2 format:
Note that the lyp should be loaded after you load your saved file to call the layer names.
'과학 (Science) > 실험과 관련된 것들' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [화학물질] 톨루엔 (Toluen), 벤진 (Benzene), (0) | 2024.11.09 |
|---|---|
| [실험] 화학 기구들 영어이름 (0) | 2024.08.14 |
| [실험] The BET method/Theory (0) | 2024.01.03 |
| [Materials] GE varnish (0) | 2023.07.07 |
| [Physical Vapor Deposition] Sputter Depositions (0) | 2023.06.24 |

댓글